We’re sharing 13 different health benefits of moderate sun exposure, including heart disease, blood pressure, diabetes, mood, an more! Plus, what the research really says about the sun and skin cancer risk…it may surprise you.
Note from Dena: This guest post was co-written by Blair Cooley, Dietetic Intern, as part of a research partnership between Back To The Book Nutrition and post-graduate nutrition students from the University of Houston.
Despite popular claims, the sun is not the enemy and there are definite benefits to moderate unprotected sun exposure. Yes, the keyword is moderate!
You might be asking, “What about skin cancer risk?” It’s a valid question and we’ll delve more into that at the end but, the evidence is clear: embracing responsible sun exposure has many health benefits.
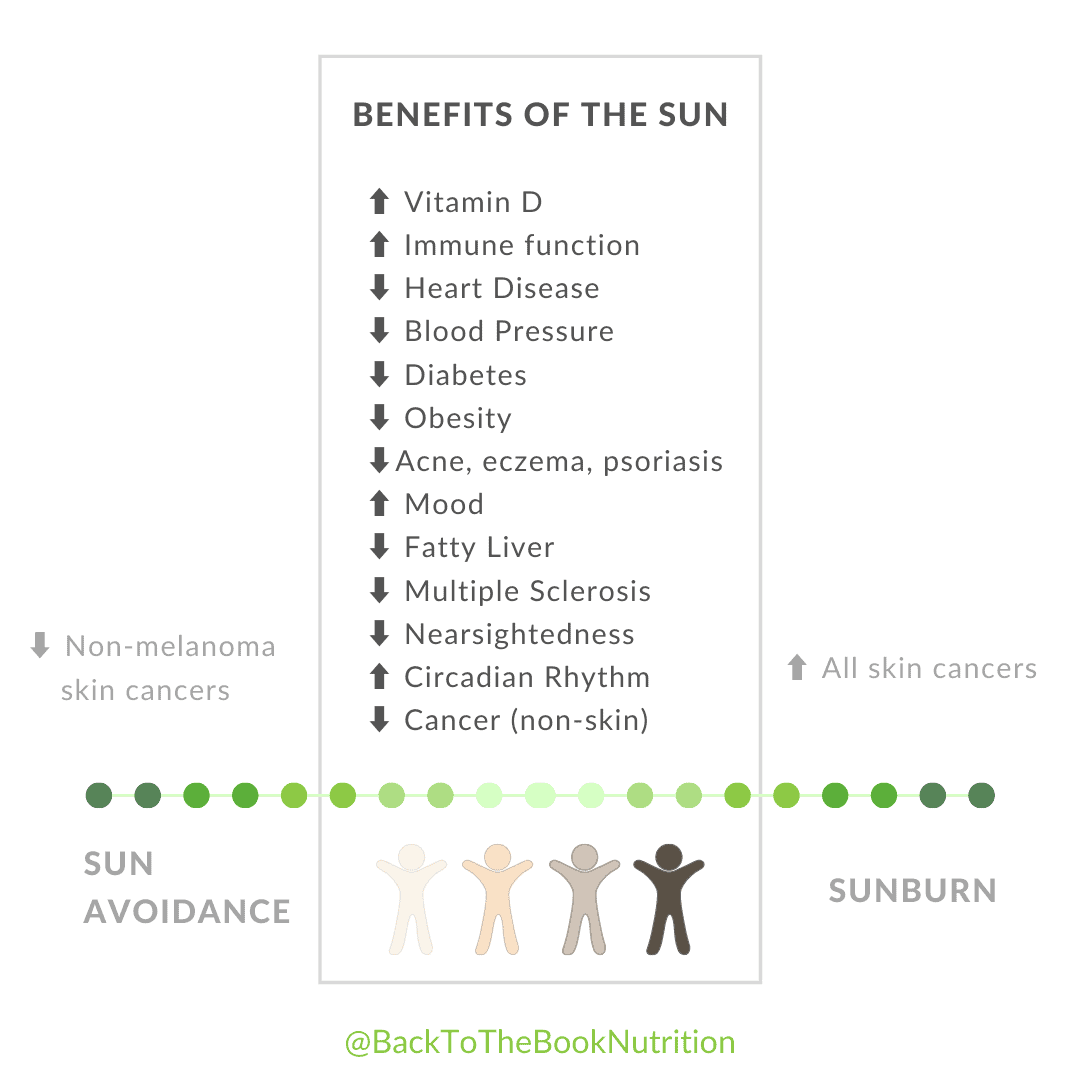
Health Benefits of the Sun
1. Raises Vitamin D Levels + Boosts Immune function
Brief, daily exposure to the sun ‘s UVB rays on about 1/3 of the body provides 80% of the vitamin D we need. Exact time depends on your skin type, latitude, and other factors, but averages 5-30 minutes per day (less for lighter skinned individuals, more for darker). What’s more, world renowned Vitamin D expert Dr. Michael Holick points out that vitamin D made in the skin (via sun exposure) lasts at least twice as long in the blood as vitamin D from the diet (1, 2).
Vitamin D strengthens your immune system and reduces risk of heart disease, cancer, autoimmune diseases, and more. (6, 7). Having adequate vitamin D levels also appears reduces risk for non-melanoma skin cancers by as much as 47% according to one study, though more study is needed to confirm this. (9)
2. Reduces Risk of Cardiovascular Death
A Swedish study found women who avoided the sun had a 60% higher death rate from cardiovascular disease compared to those who spend the most time in the sun. A related study found no association between cardiovascular death and vitamin D levels, indicating the protective effects from the sun go beyond the vitamin D it provides (3).
3. Lowers Blood Pressure
Increased sun exposure was linked to significantly lower systolic blood pressure in a study of over 300,000 African American and Caucasian dialysis patients (8). This has been demonstrated in at least one other study as well and is thought to be a result of the increased nitric oxide produced in the skin when it is exposed to sun. Nitric oxide is a potent vasodilator, expanding the blood vessels to allow blood to flow more easily (10, 11).
4. Decreases Diabetes Risk
At least one study has found ultraviolet light (sunlight), but not vitamin D supplements or 25(OH)D levels, reduced the risk of obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Interestingly, one study even showed reduced rates of Type 1 Diabetes in children whose mothers had more sunlight exposure during the 3rd trimester of their pregnancies (10).
5. Reduces Risk of Obesity
As mentioned above, at least one study has shown lower rates of obesity with higher rates of ultraviolet light exposure. This is despite lower vitamin D levels among obese individuals, suggesting benefits of sunlight apart from vitamin D (10).
6. Improves Eczema, Acne, & Psoriasis
UV light has been shown to treat psoriasis symptoms by slowing the rapid rate of skin growth and shedding that create the itchy patches. UV light can also relieve symptoms of eczema by causing the skin to release a compound that rids inflammation. The rays can also zap acne-causing bacteria, helping breakouts clear up (7). Obviously, extra care must be taken with any damaged or irritated areas so consult with an integrative dermatologist for personalized guidance.
7. Lifts Mood
When light hits your skin, it increases serotonin which boosts your mood. When you don’t get enough sun exposure, serotonin levels can drop at a rapid pace, lowering mood and even contribute to depression and seasonal affective disorder (SAD). This is especially common in latitudes that have shortened daylight hours in winter (5,7).
8. Slows Development of Fatty Liver Disease
Multiple studies have shown ultraviolet light slows the progression of fatty liver disease, both related to the vitamin D it provides and independent of it. This level of protection isn’t the same when vitamin D supplements are used (10).
9. May Decrease Multiple Sclerosis Risk and Symptoms
Multiple studies have shown a protective effect of both ultraviolet light and vitamin D against multiple sclerosis (MS). Furthermore, at least one study found that exposure to sunlight, but not vitamin D levels, were associated with less depression and fatigue among MS patients (10).
10. Reduces Nearsightedness and other Eye Health Problems
Children who spend more time outdoors are less likely to be or to become nearsighted (myopic). Nearsightedness has nearly doubled in recent decades and can lead to other problems with eye health later in life, such as retinal detachment, glaucoma, macular degeneration, and cataracts (10).
11. Improves Circadian Rhythm
Your circadian rhythm is your internal clock that responds mostly to light/dark signals that enter the eyes (not the skin). Bright light exposure in the early morning and throughout the day, as well as minimal light exposure at night, help optimize our sleep/wake cycles. Serotonin produced by daytime sunlight is also converted to melatonin at night, which doubles as an antioxidant and a sleep promoter (12, 16)
12. May Improve Hormone Balance
UV light contacting the skin directly affects hormone regulation in two ways – it communicates with the Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal (HPA) axis in the brain (and adrenals) to signal hormone production, and the skin makes sex hormones itself using cholesterol. (16, 17). More human studies are needed to determine what hormonal changes occur from different “doses” of sunlight.
13. Reduces (Non-skin) Cancer Risk
Many scientists and doctors are concerned that the focus on preventing skin cancer can potentially keep people from using sun exposure as a means to prevent other, more deadly types of cancers like lung, colon, melanoma, and breast cancer (7).
Vitamin D supplementation has had mixed results in reducing risk for the above cancers, whereas studies on blood levels of vitamin D have been more convincing. Researchers suggest this could be due to the superiority of vitamin D (and other benefits) gained from the sun versus supplements (1, 12).
But What About Skin Cancer?
Skin cancers are grouped into two main categories: Melanoma and Non-melanoma. Non-melanomas include Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC), Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC), and several other very rare types. Melanomas are about twice as deadly as non-melanomas, but still have about a 90% 5-year survival rate (as high as 98% for Stages 0,1, and 2 Melanomas but dramatically lower for stages 3 and 4). It’s important to make this distinction because not all skin cancers are the same when it comes to how deadly they are, or how the sun affects risk.
This is a vast (and very controversial) topic, but below are some of the main points: (9, 10, 12, 13, 14, 15)
- Sunburns significantly increase risk for all forms of skin cancer (more deadly melanomas as well as non-melanomas).
- Regular sun exposure darkens and thickens the epidermis (top layer of the skin), reducing sun-induced DNA damage of deeper layers.
- More time in the sun seems to increase risk for non-melanoma skin cancers SCC and BCC (though some research has questioned this link for BCC).
- Most SCC and BCC occur on constantly exposed areas (face, ears, neck, and back of hands), making these the most important for protection from sunscreen, clothing, etc.
- It’s unclear whether more time in the sun increases or decreases risk for melanoma skin cancers – Multiple human studies have shown lower rates of melanoma skin cancers among adults who spend more time in the sun compared to those who spend less time outdoors (outdoor workers vs. indoor workers, for example). A recent analysis of multiple studies where skin color was classified found that UV light did not increase melanoma risk in people with skin of color. Still, other research has shown increased rates of melanoma with chronic sun exposure. Conflicting results between studies may have to do with genetics, geography, skin color, etc. – all factors which need further research.
The Bottom Line
Obviously, there are risks and benefits to spending time in the sun. The key is to leverage the many health benefits of reasonable amounts of unprotected sun exposure while still minimizing the risks of overexposure. For more details on that, check out this post:
Sun Safety – a holistic approach
About the Co-Author:
Blair Cooley has a B.S. in Journalism and Business from the University of Missouri and completed her Post-Baccalaureate in Nutrition at the University of Houston. She is currently a Dietetic Intern who loves to cook and share her healthy, quick recipes with everyone, while having fun along the way!
Disclaimer: Information on this site is intended only for informational purposes and is not a substitute for medical advice. Always consult with a trusted healthcare provider before implementing significant dietary change. Read additional disclaimer info here.
References:






We are so sun deprived here in the winter, and I can really tell it makes a difference. I love the sun and it makes me feel so good. I would love to move somewhere tropical!
Full spectrum light boxes are inexpensive and can be a great next best during the winter months – shown to improve vitamin D levels and mood! 🙂
Thank you for this very useful article (with all the cross-references to medical blogs and articles). Gives me a lot of food for thought.
It’ so important to spend time in the sun, I can’t wait for summer!
early morning walk is the best because you get all the above mentioned health benefits out of it
Absolutely! Thanks for this, I need the reminder sometimes!
We need to get the sun every day. These amazing benefits are important for or health.
My mood definitely is lifted up, when I just sense a whiff of sunshine on me or out there. You have no idea how much I love the sunset!
Indeed sunlight has a lot of benefits. Not only for the skin but also for our overall health.
Absolutely!
The sun is indeed vital. It has many benefits. i honestly feel lonely and a little bit down when the sun is not up
A lot of people feel this way. The sun is so powerful! 🙂
It’s good to know the pros and cons of being under the sun. My parents are farmers and they have so much exposure to the sun